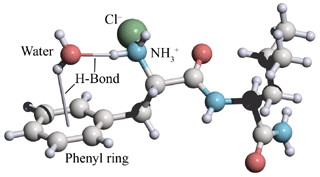
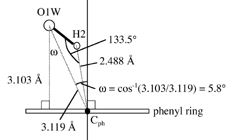
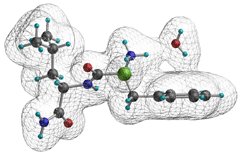
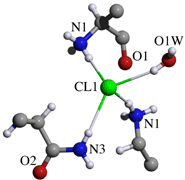
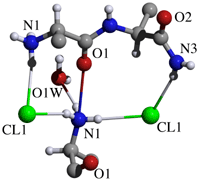
Hydrogen bonds and coordination to chloride ion
D H A D-H D...A H...A D-H...A symm. oper.
N1_1 H3_1 O1W 0.910 2.816(2) 1.945 159.5
N1_1 H4_1 Cl1 0.910 3.270(1) 2.383 164.9
N1_1 H5_1 Cl1 0.910 3.229(1) 2.357 160.4 -x+1,+y-1/2,-z+2
N1_1 H3_1 O1_1 0.910 2.686(2) 2.558 88.1 -x+1,+y-1/2,-z+2
N1_1 H4_1 O1_1 0.910 2.686(2) 2.645 82.7 -x+1,+y-1/2,-z+2
N1_1 H5_1 O1_1 0.910 2.686(2) 2.402 98.2 -x+1,+y-1/2,-z+2
O1W H1 Cl1 0.881 3.188(1) 2.343 160.9 x,+y-1,+z
N2T_2 H20_2 Cl1 0.880 3.288(1) 2.440 161.9 -x+1,+y+1/2,-z+2
O1W H1 O1_1 0.881 3.087(2) 2.788 101.5 -x+1,+y-1/2,-z+2
N2_2 H14_2 O2_2 0.880 2.919(2) 2.048 169.9 -x+2,+y-1/2,-z+2
N2T_2 H19_2 O2_2 0.880 2.915(2) 2.094 154.9 -x+2,+y+1/2,-z+2
|